In today’s technology-driven world, power inverters have become essential devices for converting DC (Direct Current) power from batteries or solar panels into usable AC (Alternating Current) power for home appliances, tools and electronics. However, with different wattage options like 220W, 350W, 150W, and 40W,It’s easy to get overwhelmed when deciding which one best suits your needs. This article provides an in-depth comparison and detailed insight into choosing the right power inverter based on wattage and requirements.
Understanding the Basics of Power Inverters
A power inverter is an electrical device that converts DC power to AC power, usually from a battery or solar panel. The output is usually in the 110-120V range, making it compatible with most household appliances and electronic devices. Key specifications to consider when choosing an inverter include:
- Input Voltage: Refers to the DC voltage the inverter requires (in this case, 18V).
- Output Voltage: The AC voltage produced by the inverter (110-120V).
- Efficiency: Indicates how effectively the inverter converts DC to AC.
Now, let’s dive into the details of each wattage option to help you decide.
40W Power Inverter: The Compact Solution
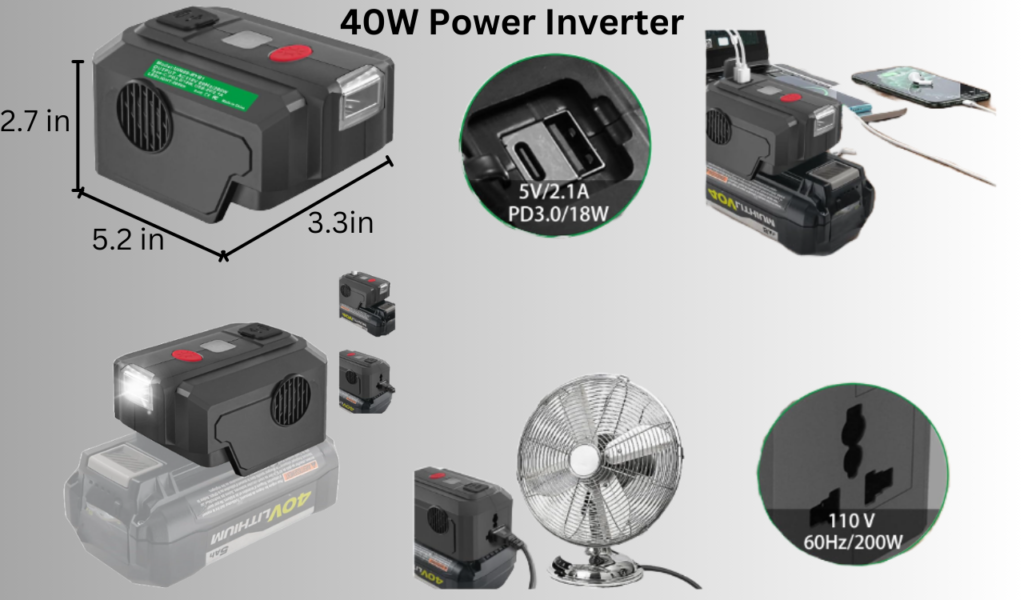
Overview
A 40W power inverter is the smallest option in the selection. It is designed for light-duty applications and is ideal for powering small devices such as mobile chargers, LED lights, or portable fans.
Use Cases
- Charging smartphones, tablets, or smartwatches.
- Powering LED strips or compact lighting systems.
- Powering small USB-powered devices while traveling.
Advantages
- Energy efficiency: consumes less power, reducing battery drain.
- Affordability: Cost-effective for basic applications.
Limitations
- Low Power Output: Not suitable for devices requiring more than 40W.
- Limited Applications: Can’t handle appliances like laptops or kitchen appliances.
150W Power Inverter: The Versatile Choice
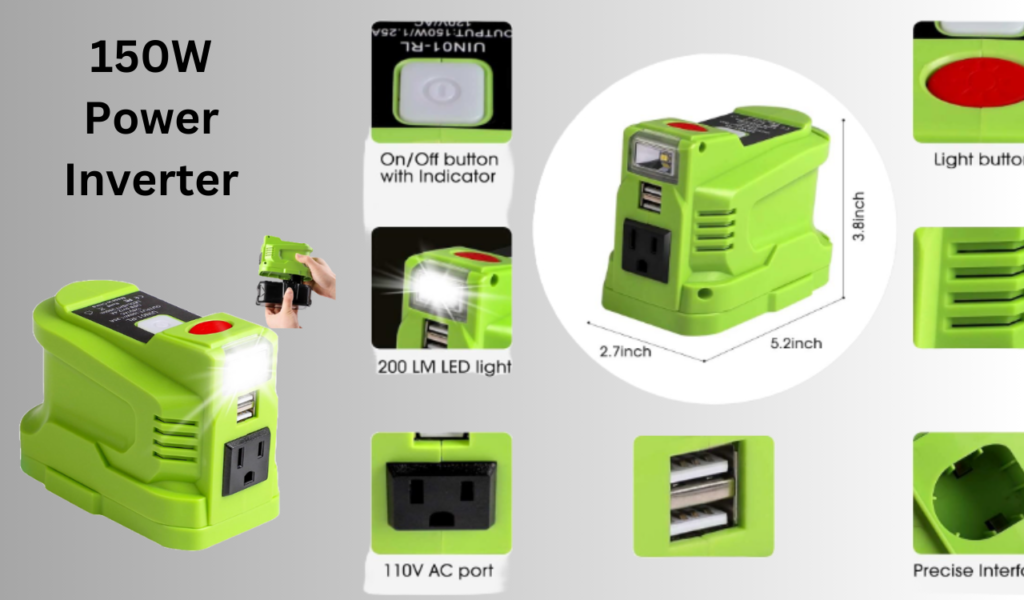

Overview
A 150W power inverter is a mid-range option that offers more flexibility. It can power a variety of small to medium devices, making it a popular choice for road trips and camping.
Use Cases
- Charging laptops, cameras, and portable game consoles.
- Powering small appliances like electric shavers or handheld vacuum cleaners.
- Operating portable medical equipment such as CPAP machines (if wattage permits).
Advantages
- Compact Design: Still portable enough for travel.
- Cost-Effective: A great balance between price and performance.
Limitations
- Limited to medium loads: Cannot handle high power appliances such as microwaves or power tools.
- Heat Generation: Prolonged use can cause overheating, requiring a cooling mechanism.
220W Power Inverter: The Everyday Performer

Overview
The 220W power inverter offers a significant step up in power efficiency. It is suitable for running multiple devices simultaneously and can handle demanding electronics.
Use Cases
- Powering laptops, monitors, and small TVs.
- Operating compact kitchen devices, such as coffee machines or blenders.
- Charging multiple devices simultaneously.
Advantages
- High Power Capacity: Can handle multiple devices at the same time.
- Wide Applications: Versatile enough for home, travel, and emergency use.
- Reliability: Often equipped with safety features such as overload protection.
Limitations
- Large Size: Slightly larger than lower wattage models.
- Higher price: Comes at a premium compared to the 40W and 150W models.
350W Power Inverter: Heavy duty option

Overview
A 350W power inverter designed for heavy duty applications. It’s ideal for users who need to power multiple devices or run power-hungry devices.
Use Cases
- Operate power tools such as a drill or soldering iron (if wattage permits).
- Operating large appliances such as mini-fridges or microwave ovens.
- Acting as a backup power source during emergency situations.
Advantages
- High Power Output: Can handle demanding appliances and equipment.
- Durability: Built to withstand heavy use.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for home, outdoor and professional use.
Limitations
- Size and weight: Larger and heavier than lower wattage options.
- Battery Drain: Consumes more power, requires a larger battery or frequent charging.
- Cost: Higher cost due to better capabilities.
Key Considerations for Selecting the Ideal Power Inverter
1.Power Requirements
Determine the energy requirements of the devices you want to power. Add up the wattage of each appliance to verify that the inverter can support the total load. For example:
- A laptop requires ~60W.
- A mini-fridge requires ~200W.
- A power drill requires ~300W.
2.Portability
If you move around a lot, choose compact and lightweight inverters like the 40W or 150W options. For stationary or emergency use, higher wattage options such as 220W or 350W are more suitable.
3.Efficiency and Battery Compatibility
Make sure the inverter matches the input voltage of your battery or power source (in this case DC 18V). High-efficiency inverters reduce energy waste while prolonging battery life.
4.Safety Features
Choose inverters equipped with integrated safety features such as:
- Overload protection.
- Short circuit prevention.
- temperature control.
5.Budget
Higher wattage inverters usually cost more. Balance your budget with your strengths to make the best choice.
Comparative Table: 40W vs 150W vs 220W vs 350W
| Feature | 40W | 150W | 220W | 350W |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Low | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Portability | Excellent | Good | Average | Low |
| Applications | Basic devices | Small appliances | Medium appliances | Heavy-duty tools |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Battery Usage | Minimal | Moderate | High | Very High |
Practical Tips for Using Power Inverters
- Avoid overloading: Never exceed the inverter’s maximum wattage capacity.
- Use quality batteries: A reliable battery ensures consistent performance and prevents damage to the inverter.
- Install a cooling system: For higher wattage inverters, ensure adequate ventilation or cooling fans to avoid overheating.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean and check the inverter periodically to ensure optimum performance.
- Use surge protectors: Protect your devices from sudden power surges.
The result
Choosing the right power inverter depends on your specific needs and usage conditions. For light duty tasks, a 40W inverter is best. If you need more versatility, a 150W or 220W inverter is ideal for small to medium appliances. For heavy duty applications, the 350W inverter is the ultimate choice.By understanding your power needs, budget, and portability preferences, you can invest in a power inverter that fits your lifestyle. With the right inverter, you’ll enjoy uninterrupted power, whether at home, on the road or outdoors.